Principles
The validation process is totally integrated to the editor.
- You cannot save an editor when a validation error is encountered..
- When displaying, modifying, saving data, the validation process is triggered.
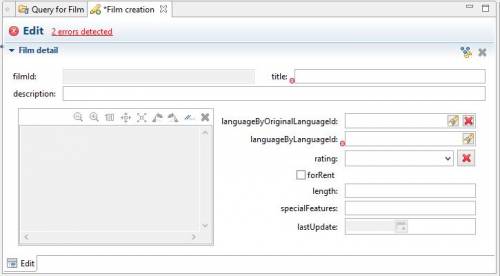
To illustrate this issue, choose in the menu the option Film / Create Film:
You can see that you obtain 2 errors corresponding to 2 mandatory fields. Each time you give a value in a field, an error is removed.
|
In fact, the attribute mandatory=“true” of fields title, languageByLanguageId is transformed as a validator during the generation process of UI classes.
|
Adding validator in XML file
For example, open file $projectDirectory/resources/xml/include/detail/FilmDIGENERATED.xml with XML editor. Change element:
<text textLimit="255" property="description" layoutData="span 3" id="description"/>
by:
<text layoutData="span 3" property="description" id="description">
<validators>
<validator key="titleLength" errorMessage="Description should not be null" warningMessage="Description generally has more than 10 characters.">
<warningWhen>return ((String) getValue()).length() < 11;</warningWhen>
<errorWhen>return null == getValue() || 0 == ((String) getValue()).trim().length();</errorWhen>
</validator>
</validators>
</text>
A validator has just been created that:
- triggers an error if the description field contains only blank characters or is a null string.
- triggers a warning (not blocking) when description text contains less than 11 characters.
Using a pre-defined validator class
Some validator could be complex or could be used in several xml files. For that, a better way is to use a predefined validator class. Syntax is:
<text property="description" layoutData="span 3" id="description">
<validators>
<validator key="titleLength" errorMessage="Description should not be null" warningMessage="Description generally has more than 10 characters.">
<errorWhen>return null == getValue() || 0 == ((String) getValue()).trim().length();</errorWhen>
<warningWhen>return ((String) getValue()).length() < 11;</warningWhen>
</validator>
<validator key="alphaNumeric" validatorClassName="org.mycompany.myproject.gencode.custom.TitleValidator"/>
</validators>
</text>
The TitleValidator class must extends the class org.adichatz.engine.validation.AValidator.
If you create the class in a subpackage of org.adichatz.gencode in source folder resources/gencode/src, you will not have to close and relaunch the application because these classes are dynamically loaded. To create the class, use the Eclipse IDE from which you launched the application.
Code could be like this:
package org.mycompany.myproject.gencode.custom;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import org.adichatz.engine.controller.IValidableController;
import org.adichatz.engine.controller.field.TextController;
import org.adichatz.engine.validation.AValidator;
import org.eclipse.jface.dialogs.IMessageProvider;
public class TitleValidator extends AValidator {
public TitleValidator(IValidableController triggeringController, String key) {
super(triggeringController, key);
}
@Override
public int validate() {
String title = (String) ((TextController) triggeringController)
.getValue();
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("(\\w| )+");
if (null != title && !pattern.matcher(title).matches()) {
return setLevel(IMessageProvider.ERROR,
"Only alphanumeric characters are accepted.");
} else
return setLevel(IMessageProvider.NONE, null);
}
}
A validator has just been created. The validator triggers an error when the title don't have an alphanumeric value.